Ultrasound technicians play a vital role in the allied healthcare industry, using specialized equipment to capture images that aid in diagnosing and treating patients. We will aim to guide you on how to become an ultrasound technician, emphasizing the importance of education, training, and certification in unlocking opportunities and career advancement.
Prerequisites for Becoming an Ultrasound Tech
The prerequisites for becoming an ultrasound technician, also known as a diagnostic medical sonographer, can vary depending on the specific program and the level of certification desired. However, common prerequisites include:
- Education: Most ultrasound technician programs require a minimum of a high school diploma or equivalent. Some programs may also require specific coursework in subjects such as math, science, and anatomy.
- Prerequisite Courses: Many programs require applicants to have completed certain prerequisite courses, such as biology, chemistry, physics, and anatomy and physiology. These courses provide a foundation in the sciences relevant to ultrasound technology.
- Clinical Experience: Some programs may require or prefer applicants to have prior healthcare or clinical experience. This can include work as a nursing assistant, medical assistant, or in another healthcare role.
- Certification and Licensure: While not always a prerequisite for entry into a program, most employers require ultrasound technicians to be certified. Certification is typically obtained through organizations such as the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS) or the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT).
- Background Check and Immunizations: Many programs require applicants to undergo a background check and provide documentation of up-to-date immunizations.
- Technical Skills: Applicants should have strong technical skills, including the ability to operate and troubleshoot ultrasound equipment.
- Communication Skills: Effective communication skills are important for working with patients and healthcare professionals.
- Physical Requirements: Ultrasound technicians may need to lift or assist with moving patients, so physical strength and dexterity may be important.
It’s important to check the specific requirements of the program you are interested in, as they can vary. Additionally, some programs may have additional requirements or preferences for admission.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Seattle University
Bachelor of Science in Diagnostic Ultrasound
What is an Ultrasound Technician?
An ultrasound technician, also known as a diagnostic medical sonographer, is a healthcare professional who uses specialized equipment to create images of the body’s internal structures. These images, known as sonograms or ultrasounds, help physicians diagnose and treat various medical conditions. There are different types of ultrasound technicians, such as vascular sonographers, who specialize in imaging blood vessels, and obstetric and gynecologic sonographers, who focus on the female reproductive system.
Ultrasound technicians typically work in hospitals, outpatient care centers, and physicians’ offices. They often spend long hours on their feet and may need to lift or move patients during examinations. The job outlook for ultrasound technicians is positive, with the Bureau of Labor Statistics projecting a 10% growth in employment between 2022 and 2032, which is much faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is mainly attributed to the increasing use of ultrasound imaging as a safer, non-invasive alternative to traditional radiological procedures.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Washburn University (Online)
1-Year Advanced Certificate Program in three (3) areas:
- OB/GYN Sonography
- Cardiac sonography
Vascular sonography
Education Requirements for Ultrasound Technicians
Starting in high school, aspiring ultrasound technicians should focus on courses in science, such as biology, physics, and mathematics. These subjects provide a solid foundation for the post-secondary education required to become an ultrasound technician. There are three main post-secondary education options: certificate programs, associate degree programs, and bachelor’s degree programs. The best path into this career would be a program in either Diagnostic Medical Sonography or Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography. We break down these programs below.
Certificate programs often take around 1-2 years to complete. They are typically the shortest in length of the available programs. These programs are suitable for individuals who already have a background in healthcare or a related field. They provide focused training in ultrasound technology and clinical practice.
Associate degree programs in diagnostic medical sonography usually take about two years to complete. These programs offer a more comprehensive education and include general education courses along with ultrasound-specific coursework. They are a common choice for students entering the field with little to no prior healthcare experience.
Bachelor’s degree programs typically take 4 years to complete and offer a more in-depth education. They may include advanced coursework in ultrasound specialties and research opportunities. These programs are suitable for those who want to advance their careers in sonography and potentially pursue leadership or teaching roles in the field.
Key subjects covered in ultrasound technician programs include anatomy, physiology, patient care, medical ethics, and sonographic imaging techniques. Practical, hands-on experience with ultrasound equipment is also an essential component of these programs.
It is crucial to choose an accredited program, as this ensures the quality of education and increases the likelihood of finding employment after graduation. The Commission on Accreditation of Allied Health Education Programs (CAAHEP) is the primary accrediting body for ultrasound technician programs in the United States. Accredited programs typically include a combination of classroom instruction, laboratory work, and clinical experience.
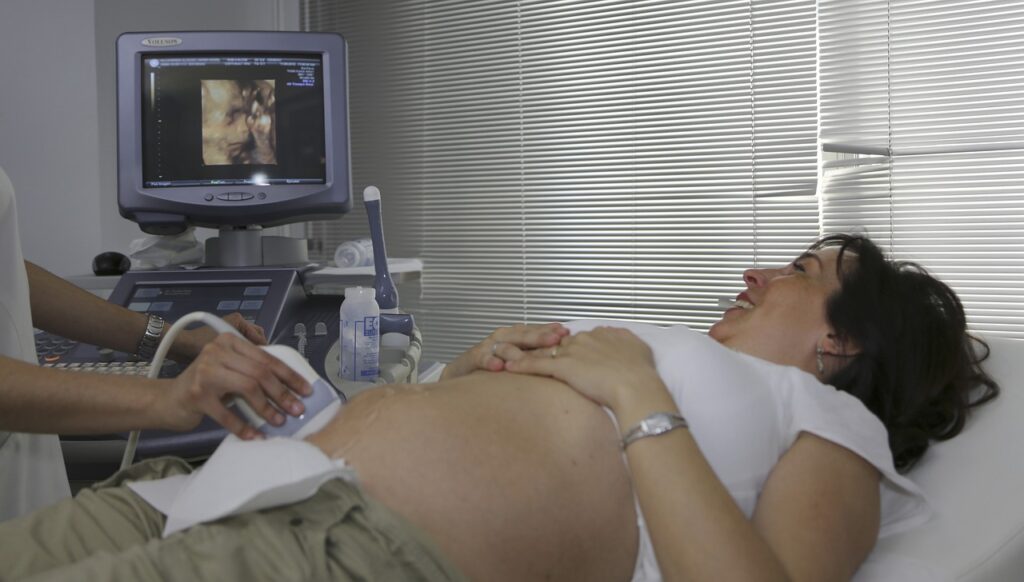
Classes for Ultrasound Technicians
In an ultrasound technology program, students typically take a variety of courses designed to prepare them for a career as an ultrasound technician. These courses cover both theoretical knowledge and practical skills related to ultrasound imaging. Some common courses include:
- Anatomy and Physiology: This course covers the structure and function of the human body, including organs and systems relevant to ultrasound imaging.
- Medical Terminology: Students learn the language used in healthcare settings to describe anatomy, diseases, and medical procedures.
- Ultrasound Physics and Instrumentation: This course covers the principles of ultrasound imaging, including how ultrasound waves are produced, how they interact with tissue, and how images are formed.
- Sonographic Principles and Instrumentation: Building on ultrasound physics, this course focuses on the operation of ultrasound equipment and the techniques used to obtain quality images.
- Abdominal Sonography: Students learn to perform and interpret ultrasound scans of the abdomen and its organs, such as the liver, gallbladder, and kidneys.
- Obstetric and Gynecologic Sonography: This course covers the use of ultrasound in pregnancy and women’s health, including fetal development and monitoring.
- Vascular Sonography: Students learn to perform ultrasound scans of the blood vessels to evaluate blood flow and detect abnormalities.
- Clinical Practicum: In addition to classroom instruction, students participate in clinical rotations where they gain hands-on experience performing ultrasound scans under the supervision of experienced technologists.
- Patient Care and Ethics: This course covers topics such as patient communication, medical ethics, and legal issues related to healthcare.
- Pathophysiology: Students learn about the nature and progression of disease processes, which helps them understand the clinical significance of ultrasound findings.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Pima Medical Institute
Diagnostic Medical Sonography Associate Degree Program
Training and Clinical Experience
Hands-on training is critical to becoming an ultrasound technician, as it helps students develop the necessary skills to operate ultrasound equipment and interpret images effectively. Most ultrasound technician programs require students to complete a certain number of clinical hours to gain practical experience in real-world settings.
Clinical experience requirements vary depending on the program but typically involve working under the supervision of experienced professionals in hospitals or other healthcare facilities. This hands-on experience allows students to apply their classroom knowledge to real patients and develop their technical, communication, and critical thinking skills.
Internships and job shadowing opportunities can provide valuable insights into the day-to-day responsibilities of an ultrasound technician and help students establish professional connections in the field. These opportunities may be available through the student’s educational program or by reaching out to local healthcare facilities.
Volunteer work at hospitals, clinics, or community health events can also help aspiring ultrasound technicians gain experience, demonstrate their commitment to the field, and expand their professional network. Such experiences can be particularly beneficial when seeking employment after completing an ultrasound technician program.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Saint Joseph’s University
Associate Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography
Certification and Licensure
There are several certification options for ultrasound technicians, including the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS), Cardiovascular Credentialing International (CCI), and the American Registry of Radiologic Technologists (ARRT). While certification is not always required, it can significantly enhance career advancement and job opportunities, as many employers prefer or require certified candidates.
To obtain certification, candidates must meet eligibility requirements, such as completing an accredited ultrasound technician program and gaining a specific amount of clinical experience. The next step is passing a certification examination, which typically covers topics such as sonographic principles, instrumentation, and specialty-specific knowledge.
Certification demonstrates a technician’s commitment to maintaining high standards of practice and staying current in the field. It can lead to increased salary potential, better job opportunities, and greater professional recognition.
Some states may also require licensure for ultrasound technicians, though this is not as common as certification. Licensure requirements vary by state and may include completing an accredited program, passing a state-specific examination, and maintaining continuing education credits. It is essential to check with the state in which you plan to work for specific licensure requirements.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Baker College
Associate of Applied Science Diagnostic Sonography (Abdomen/OB-GYN)
Continuing Education and Professional Development
Staying up-to-date with the latest advancements in the ultrasound technician field is vital for maintaining expertise and providing high-quality patient care. Continuing education options include workshops, conferences, online courses, and seminars, which can help technicians stay current with industry trends and advancements in technology.
Many certification organizations, such as ARDMS and CCI, require ultrasound technicians to earn Continuing Medical Education (CME) credits to maintain their certification. CME credits can be obtained through various activities, including attending conferences, participating in workshops, or completing accredited online courses.
Networking and joining professional organizations, such as the Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonography (SDMS), can also be beneficial for ultrasound technicians. These organizations provide opportunities to connect with peers, share knowledge, and stay informed about the latest research and developments in the field. Additionally, membership in a professional organization may offer access to exclusive resources, job boards, and discounts on continuing education courses.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Rochester Institute of Technology
Bachelor of Science Degree in Diagnostic Medical Sonography (Ultrasound)
Tips for Success in the Ultrasound Technician Career
Developing strong communication and interpersonal skills is crucial for ultrasound technicians, as they need to effectively explain procedures to patients, collaborate with physicians, and convey imaging results. These skills contribute to a positive patient experience and ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment.
Staying organized and managing time effectively is essential for ultrasound technicians, given their demanding work schedules and the need to balance multiple patients and responsibilities. Good time management can lead to increased efficiency, reduced stress, and a more balanced work-life experience.
Embracing technology and staying current with industry advancements is critical for ultrasound technicians, as new techniques and equipment can improve diagnostic accuracy and patient care. Continuously learning about new developments in the field can help technicians stay ahead and maintain their expertise.
Pursuing specialization and advanced certifications can open up new opportunities and enhance career growth. Specialization allows technicians to focus on specific areas of interest and expertise, such as vascular, pediatric, or musculoskeletal sonography, setting them apart from other professionals in the field. Advanced certifications can demonstrate a technician’s commitment to excellence and proficiency in their specialized area, leading to increased job opportunities and higher salary potential.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Bismarck State College
Diagnostic Medical Sonography (Ultrasound)
Diagnostic Medical Sonography vs. Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography
Diagnostic Medical Sonography (DMS) and Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography (DCS) are both specialized fields within the broader discipline of medical ultrasound technology. While they share some similarities in terms of using ultrasound technology to create images of the body’s internal structures, they have distinct focuses and areas of specialization. Here are the key differences between Diagnostic Medical Sonography and Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography programs:
Diagnostic Medical Sonography (DMS)
- Focus: DMS programs train students to perform ultrasound examinations on various parts of the body, including the abdomen, pelvis, vascular system, and musculoskeletal system. DMS encompasses a wide range of applications beyond the heart.
- Specialization: DMS programs may offer specialization options in areas such as abdominal sonography, vascular sonography, obstetric and gynecologic sonography, breast sonography, or musculoskeletal sonography, among others. Students can choose a specific area of interest based on their career goals.
- Clinical Training: Clinical rotations in DMS programs expose students to a diverse range of ultrasound procedures, allowing them to gain experience in multiple areas of diagnostic imaging.
- Certification: Graduates of DMS programs are eligible to pursue certification as Registered Diagnostic Medical Sonographers (RDMS) through organizations like the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). Certification may be obtained in one or more specialty areas.
- Career Opportunities: DMS graduates can work in a variety of healthcare settings, including hospitals, clinics, imaging centers, and private practices. They can perform ultrasound scans for diagnosing conditions in multiple body systems.
Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography (DCS)
- Focus: DCS programs specifically focus on the heart and circulatory system. Students learn to perform echocardiograms (ultrasound examinations of the heart) to assess its structure and function, as well as to evaluate blood flow through the heart’s chambers and vessels.
- Specialization: DCS programs typically do not offer as much specialization as DMS programs. The primary focus is on cardiac ultrasound, although some programs may include basic training in vascular ultrasound.
- Clinical Training: Clinical rotations in DCS programs primarily involve hands-on experience with cardiac ultrasound procedures. Students work with patients to capture images of the heart for diagnostic purposes.
- Certification: Graduates of DCS programs can pursue certification as Registered Diagnostic Cardiac Sonographers (RDCS) through organizations like the American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography (ARDMS). This certification specifically validates their competence in cardiac ultrasound.
- Career Opportunities: DCS graduates are primarily qualified to work in cardiology departments of hospitals, heart clinics, and other healthcare facilities that specialize in cardiovascular care. They play a crucial role in diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions.
In summary, the main difference between Diagnostic Medical Sonography and Diagnostic Cardiac Sonography programs lies in their scope of practice and specialization. DMS programs cover a broader range of ultrasound applications across different body systems, while DCS programs are specifically tailored to cardiac ultrasound imaging and focus on the heart and its associated structures. Students should choose a program that aligns with their career interests and goals in the field of medical ultrasound.

Ultrasound Technician Programs from The College of Healthcare Professions
Diagnostic Medical Sonography – Associate of Applied Science Degree Program
Ready To Become an Ultrasound Tech?
Becoming an ultrasound technician involves completing high school prerequisites, pursuing post-secondary education through certificate, associate, or bachelor’s degree programs, gaining hands-on training and clinical experience, and obtaining certification. Those interested in pursuing a career as an ultrasound technician should be encouraged by the rewarding nature of the profession and the positive job outlook. Emphasizing the importance of education, training, and certification can unlock numerous opportunities and career advancement for aspiring ultrasound technicians.
For more information on education pathways and career advice, visit Pathways2Advancement.org, where you can find valuable resources and guidance to help you on your journey towards a successful career in the healthcare industry.
Resources for Aspiring Ultrasound Technicians
Diagnostic Medical Sonography Schools: https://www.caahep.org/students/find-an-accredited-program
*Be sure to click “diagnostic medical sonography” under the profession category.
American Registry for Diagnostic Medical Sonography: https://www.ardms.org/discover-ardms/career-center/sonography-resources/
Society of Diagnostic Medical Sonography: https://www.sdms.org/resources/educational
Rutgers University: https://libguides.rutgers.edu/c.php?g=716415&p=5098092

Ultrasound Technician Programs from Hinds Community College
Associate of Applied Science in Diagnostic Medical Sonography